Study: Curcumin, a polyphenol in turmeric, can selectively target cancer stem cells
03/14/2019 / By Tracey Watson

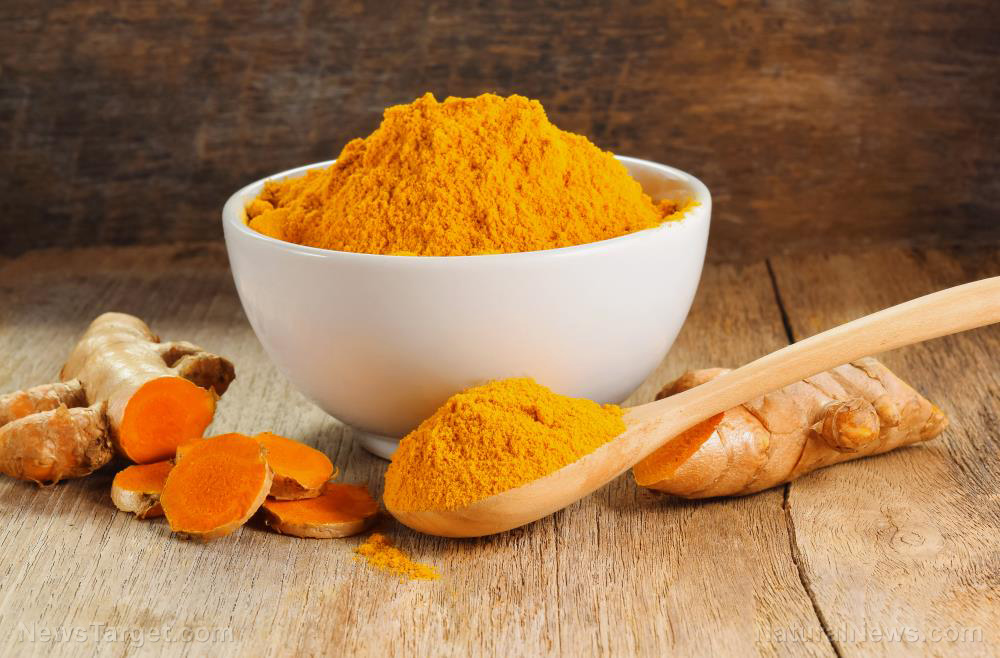
In the world of health foods and superfoods there are some that stand head and shoulders above the rest and could almost be labeled “miracle foods.” One of the most well-known of these amazing foods is curcumin, the polyphenol that gives turmeric its beautiful, bright yellow color.
Used for thousands of years in ancient Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, turmeric – thanks to powerful compounds known as curcuminoids – has powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory powers. Over 240 studies have also confirmed that the curcumin in turmeric boosts brain power and lowers risk of brain diseases; reduces risk of heart disease; prevents and possibly even helps to treat Alzheimer’s disease; reduces arthritis symptoms; helps ward of depression; and fights the effects of aging. (Related: The powerful health benefits of curcumin.)
However, despite all these amazing health benefits, it is perhaps curcumin’s ability to both prevent and treat cancer that has researchers most excited. Now, a groundbreaking study published in the journal Anticancer Research has revealed that curcumin can selectively target and destroy the stem cells that cause cancer malignancy – without destroying healthy cells in the process.
“Smart kill” properties that leave chemo and radiation in the dust
As explained by Green Med Info’s Sayer Ji, cancer stem cells (CSCs) are the only cells capable of producing all the other types of cells found within a malignant tumor. They are therefore the most lethal of all the cell types in most cancers.
These cells are true killers, super resistant to both chemotherapy and radiation, and even spread by surgery. Experts believe that they are the primary cause of the failure of conventional cancer treatments and cancer recurrences.
The study identified no fewer than eight different ways in which curcumin targets and destroys these dangerous cells, including:
- Down-regulation of interleukin-6 (IL-6): IL-6 is a cytokine which modulates immunity and inflammation, and may be the link between inflammation progressing to cancer.
- Down-regulation of interleukin-8 (IL-8): Another cytokine, the body releases IL-8 after tumor cell death, which in turn stimulates CSCs to regrow the tumor. It also enhances chemotherapy resistance.
- Down-regulation of interleukin-1 (IL-1): IL-1 is the cytokine which responds to injury and infection, and plays an important role in the stimulation of CSCs and the growth of cancer cells.
In addition, curcumin was also found to interfere with the binding of two proteins called CXCR1 and CXCR2. It also modulates the Wnt signaling pathway, the Notch signaling pathway, the Hedgehog pathways and the FAK/AKT/FOXo3A pathway.
In laymen’s terms, curcumin is a super weapon that targets cancer stem cells in eight different ways, making it an unstoppable cancer destroyer. Even if the science is a little complicated, the bottom line is not. (Related: Curcumin slays cancer cells in their tracks.)
The best way to increase curcumin intake
When it comes to curcumin, there are a few important things to remember.
Firstly, curcumin is only found in very small amounts in turmeric, so while adding turmeric to meals is a great idea, to really derive all of its health benefits, it is probably best to take a high-quality curcumin supplement derived from organic, lab-tested turmeric that’s been verified to be low in heavy metals (turmeric often contains lead if grown in contaminated soils).
Secondly, the body does not absorb curcumin well. Fortunately, there is a way to increase bio-availability. When consuming black pepper with curcumin absorption is increased by an astounding 2,000 percent! Since curcumin is fat soluble, it is also advisable to take it with a fatty meal.
Irrespective of how you choose to increase your curcumin intake, your body will reward you many times over with improved health now and in the future.
Discover more of the many amazing natural ways to prevent and treat cancer at CancerSolutions.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: cancer, cancer stem cells, cancer treatment, chemo, CSCs, curcumin, food cures, food science, Herbs, miracle food, natural medicine, polyphenols, research, science, TCM, turmeric