Organic hemp protein helps you reach the high point of your health
02/08/2022 / By Olivia Cook
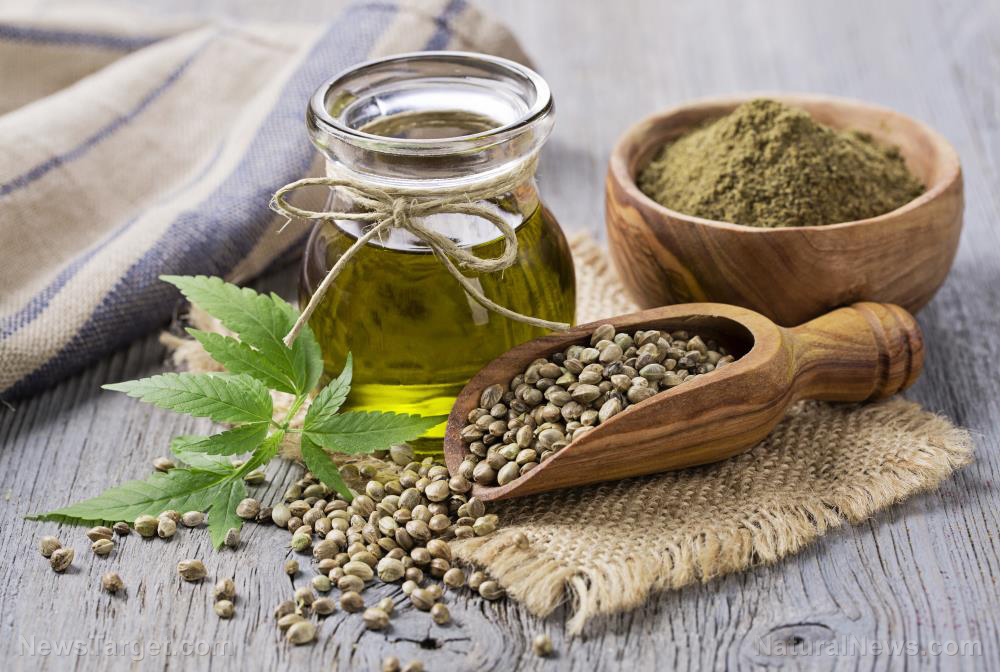

Hemp is a magnet for controversy largely because of its origins, which is often misunderstood. While hemp and marijuana are from the same Cannabis genus, they are genetically distinct forms of cannabis that are distinguished by their use and chemical composition, as well as differing cultivation practices used in their production.
Unlike marijuana, hemp does not produce psychoactive effects in its users.
High levels of a cannabinoid called tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are found in marijuana, which is responsible for eliciting the “high” it produces. Hemp, on the other hand, only contains less than 0.3 percent THC.
Since the late 1950s, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has strictly controlled and regulated hemp production. Prior to the late 1950s, hemp in the U.S. was considered an agricultural commodity, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) supported its production.
Restrictions on U.S. hemp production and marketing were relaxed by changes enacted in the 2014 Agricultural Act and were relaxed even more by the 2018 Agricultural Act, which provides further differentiation between [industrial] hemp and marijuana in terms of farm policy and federal regulatory oversight.
Health benefits of hemp protein
Hemp protein is recognized as having excellent nutritional value in promoting growth, replacing the loss of essential nutrients, providing energy and assisting in the efficient function of nutritional and other metabolic processes necessary for human existence. (Related: Hemp protein: Eat the nutrients.)
Supports a healthy immune system
Hemp seeds contain edestin and albumin, globular proteins that are essential to supporting a healthy immune system. Enzymes, antibodies, hormones and fibrinogen are all made from globular proteins.
Supports a healthy musculoskeletal system
Hemp protein contains threonine, an essential amino acid that helps keep the connective tissues and muscles throughout the body, including the heart, strong and elastic. It also helps build strong bones and may speed wound healing or recovery from injury.
Supports brain health
Hemp contains phenylalanine, an essential amino acid that the body can convert into tyrosine, which it then uses to synthesize the brain neurotransmitters dopamine (a brain chemical messenger that has important roles in sleep and memory, as well as metabolism and emotional well-being) and norepinephrine or noradrenaline (a compound that plays a role in the regulation of the sympathetic nervous system).
Supports cardiovascular health
Hemp protein contains high amounts of the amino acids arginine, which is used for the production of nitric oxide – a gaseous substance in the body that causes the blood vessels to expand. This, in turn, leads to lowered levels of blood pressure, reducing the risk of health disease.
Supports healthy digestive function
Hemp seeds contain contain the amino acids cysteine and methionine, which stimulate the liver to remove the toxins from the body.
Hemp also has the perfect ratio of omega fatty acids that help maintain the body’s pH balance. Its essential fatty acids help to retain oxygen in the cell membranes, which act as barriers to toxins. It has soluble and insoluble fiber, which both help to cleanse the colon and intestinal tract and remove toxins.
Hemp’s high fiber concentration can reduce constipation, protect the gut and lower your risk of developing diarrhea or hemorrhoids.
Supports healthy skin, hair and nails
Methionine, a sulfur-containing amino acid in hemp protein, improves the tone and elasticity of the skin, promotes healthy hair and strengthens nails. This amino acid protects the cells from pollutants, facilitates the detoxifying process, slows down the aging process and helps with the absorption of other nutrients.
Hemp is also loaded with omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids that promote healthy hair growth. It naturally conditions the scalp because it also contains vitamin E.
Supports healthy sleep patterns
Hemp is a great source of magnesium, which acts as a cofactor or helper molecule in more than 600 biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle movements – contraction and relaxation – preparing the body for rest and rejuvenation.
Uplifts mood naturally
Tryptophan, an essential amino acid in hemp protein, produces niacin (also known as vitamin B3), which is essential in creating the brain neurotransmitter serotonin – a natural mood stabilizer.
Supports sensible weight management
As a high-protein source, hemp protein powder prevents protein deficiency. Supporting healthy protein levels can boost the metabolism, as well as increase fat-burning potential.
Supports healthy energy levels
Hemp protein contains valine, leucine and isoleucine – three branched-chain amino acids that enhance energy, increase endurance and aid in muscle tissue recovery and repair. Hemp also contains essential fatty acids. When ingested, these fatty acids produce twice as much energy as carbohydrates.
What you can do with hemp protein
Hemp is consumed in many forms, including protein powder, flour or meal. Because hemp products don’t contain gluten, they are a good alternative to wheat products.
Hemp protein powder is one of the best sources of protein you can use for your recipes. It has an earthy, nutty taste and offers plenty of health benefits. Use it to make the following healthy foods and drinks: (Related: Nutiva’s new hemp protein boasts best taste, easier mixing.)
Smoothies and shakes. Hemp protein is the best grain-free, gluten-free powder for smoothies and shakes. It’s best consumed blended with other ingredients since it can have a grittier texture than other plant-based proteins.
Brownies. Though hemp seeds tend to taste a bit earthy, hemp protein powder has a much different flavor that can be easily blended with other ingredients to make delicious brownies. All you need to do is replace regular flour with hemp protein and cocoa powder. Use equal amounts of both and whatever other ingredients you normally use in your brownies.
Grain-free cereal. You can consume hemp protein powder for breakfast in a grain-free recipe. All you need to do is stir one scoop of hemp protein powder (about 3 tablespoons) with a little healthy thickening agent, such as tapioca (2 tablespoons tapioca flour to substitute for 1 tablespoon of cornstarch), a natural sweetener of your choice, non-dairy milk and any spices you would like, such as cinnamon, ginger or cardamom. You can also add chia and flax for more omega-3s. Stir to make a thick, pudding-like cereal and enjoy the filling benefits of this amazing easy-to-digest breakfast.
Raw energy bites. Aside from hemp seeds, hemp protein is also a great ingredient in raw energy bites with one extra benefit: It is a better binder than plain hemp seeds due to its flour-like consistency. You can easily mix it with some non-dairy milk or water, some sweetener of your choice, a little almond or cashew butter, some raw coconut shreds, perhaps some cacao and whatever spices you enjoy. Stir and mix them all up. Roll into small bite-sized balls with your hands. You now have protein-filled energy bites without the need for dried fruit as a binder.
Whether you’re looking to increase your intake of healthy fats or just searching for something natural to use on your skin, hair and nails, consider hemp protein because it has the potential to keep you healthy, youthful and radiant.
More Related Stories:
Hemp Protein: Eat the Nutrients.
London cafes now sell 100% organic hemp milk that helps relieve stress, anxiety, pain and insomnia.
Hemp seeds are excellent sources of protein, fiber and fatty acids.
Watch the video below to know why organic hemp is the best source of plant-based protein.
This video is from the Health Ranger Store channel on Brighteon.com.
Check out HempScience.news for more on the benefits offered by hemp products.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
Amino Acids, brain health, cannabis, digestion, essential fatty acids, fitness, food is medicine, food science, heart health, hemp, hemp protein, immune system, mental health, natural ingredients, nutrients, skin care, sleep, supplements, weight management
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 FOOD SCIENCE NEWS