Maintain a healthy weight and lower heart disease risk with the natural dietary fiber glucomannan
10/04/2023 / By Olivia Cook
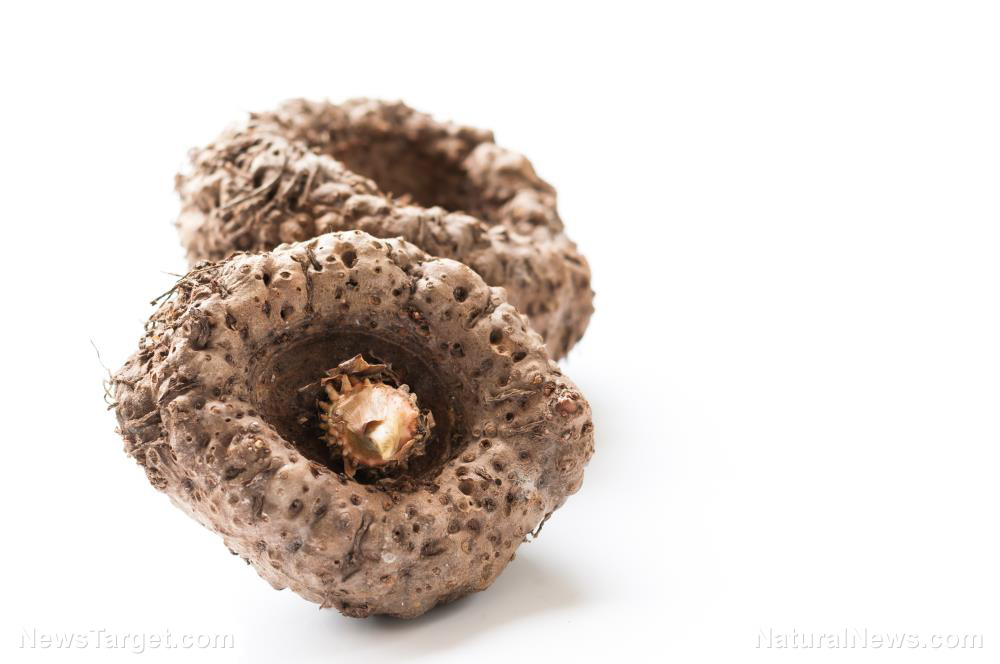

Glucomannan is a natural dietary fiber sourced from the roots of the konjac (Amorphophallus konjac), also called the Japanese elephant yam. The konjac root, which is dried and ground up, is commonly used in Asia as both a food thickener and medicine.
Glucomannan does the following to support healthy weight management and lower heart disease risk:
Naturally curbs appetite and promotes satiety
Glucomannan creates bulk because it has the highest viscosity of any known natural fiber. It takes up physical space in the stomach, contributing to satiation and turning off the brain’s hunger signals. This feeling of fullness leads to a reduced calorie intake.
Glucomannan also forms a protective film along the bowel wall, prolonging the time food remains in the stomach, which promotes feelings of fullness and reduces hunger pangs. This, in turn, leads to reduced food intake.
Glucomannan also contains no calories – just fiber. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition looked at the effects of glucomannan noodles used as an alternative to carbohydrate-rich noodle varieties. Researchers found that consuming glucomannan noodles reduced calorie and carbohydrate levels and eliminated the need to consume additional calories. (Related: Shirataki noodles, a low-carb and low-GI superfood perfect for vegans.)
Lowers glycemic index
Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) – those with a GI value of 55 or less – have a weaker effect on blood sugar. GI measures how slowly and steadily or quickly certain foods increase blood glucose levels.
Eating high-GI foods causes excess insulin production and results in fat creation and storage. This also translates to hunger as blood sugar crashes following the glucose spike.
In contrast, consuming low-GI foods contributes to more stable blood sugar levels – minus the hunger spikes, mood swings and blood sugar fluctuations. It also protects the pancreas and inhibits the storage of body fat.
Combining glucomannan with foods eaten regularly effectively lowers the GI of these foods. This is because glucomannan slows the absorption of carbohydrates and sugars from those foods.
Reduces blood cholesterol and blood sugar
The sticky, viscous quality of glucomannan helps manage blood cholesterol and blood sugar levels. This natural fiber from the konjac root holds on to carbohydrates and sugars in the stomach and delays their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. The reduction of blood glucose and blood cholesterol levels is due to the slowed stomach emptying which leads to higher absorption of nutrients by the small intestine and increased insulin sensitivity.
This is evidenced in a study published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules which showed that consuming glucomannan before a meal slows down cholesterol and sugar absorption and prevents the spike of insulin after. Slowing down this insulin spike helps reduce blood sugar levels, with the resulting decrease in insulin resistance contributing to weight loss.
Supports healthy digestion
For constipation, glucomannan can start peristalsis – a series of wave-like muscle contractions that help food move easily through the digestive tract and support normal bowel function. Glucomannan also positively impacts beneficial gut bacteria which secrete chemicals that help regulate food cravings, immune function, digestive function, metabolism and more.
Glucomannan also acts as a prebiotic – capable of improving the health of your gut microbiome by protecting beneficial bacteria, according to a study published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. Glucomannan travels to the lower digestive tract and becomes a food source for the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Meanwhile, a separate study published in Alternative and Complementary Therapies noted how glucomannan can help those suffering from chronic inflammation, leaky gut syndrome, ulcers and other gastrointestinal disorders.
Visit FoodIsMedicine.com for more stories about the health benefits of glucomannan in konjac.
Watch this video that explains what is glucomannan.
This video is from the Natural Cures channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Glucomannan consumption can help protect gut epithelial homeostasis.
What you need to know about glucomannan and its usefulness as a weight loss supplement.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
#nutrition, diabetes cure, dietary fiber, digestion, fight obesity, food cures, food is medicine, food science, glucomannan, health science, heart disease, heart health, konjac, natural cures, natural health, natural medicine, nutrients, prevent diabetes, prevention, slender, supplements, weight loss
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 FOOD SCIENCE NEWS